Welding Wire Leads Carbon Footprint, Fronius Study Finds

Fronius has unveiled a new Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) initiative, set to redefine sustainability standards in the welding industry. With a focus on reducing carbon footprint and promoting eco-friendly production, Fronius is pushing for greener manufacturing processes and sustainable welding technologies.
The new LCA methodology assesses the environmental impact of each product from raw material extraction to disposal, offering a detailed analysis of carbon footprints.
By adopting these strategies, Fronius not only aims to enhance transparency in the industry but also sets a new global benchmark for sustainable welding.
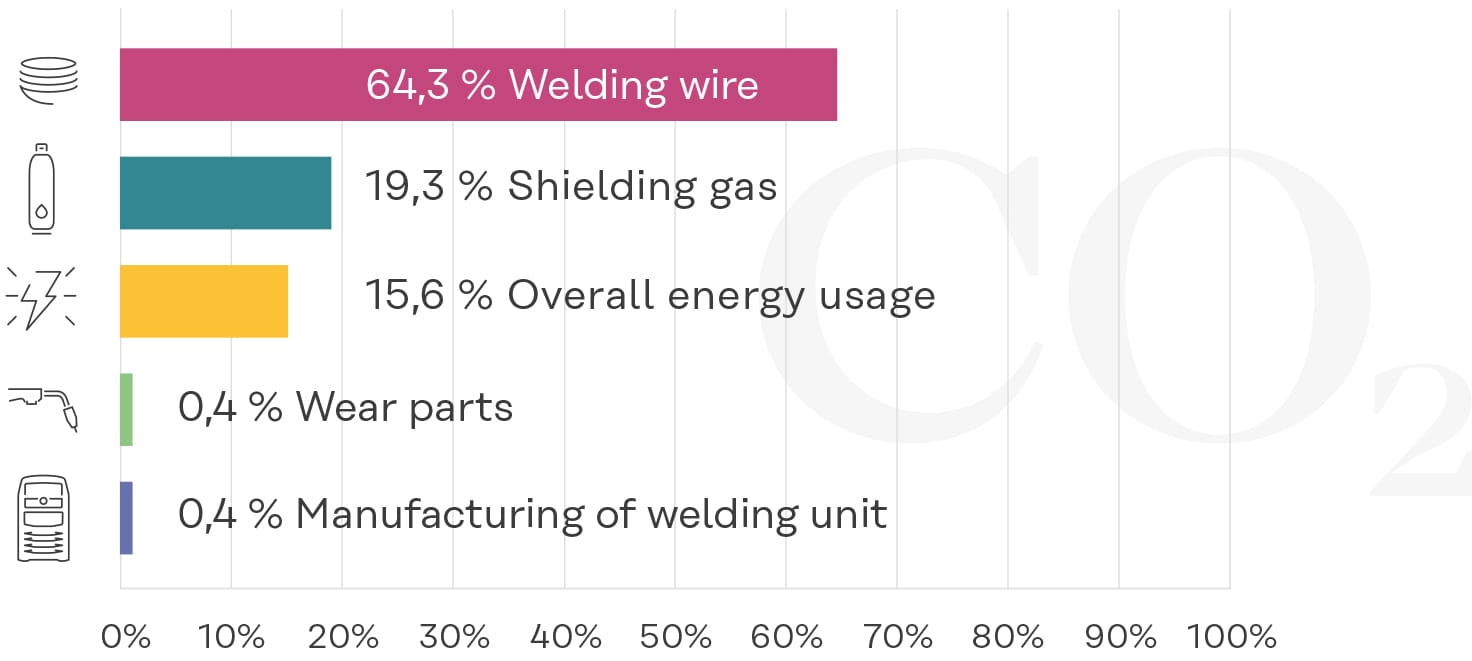
This Chart from Fronius shows the distribution of carbon footprints from welding processes and reveals that the majority of emissions (64.3%) are caused by the use of welding wire. Shielding gas is second with 19.3%, followed by general energy use with 15.6%. Effects from the manufacture of wear parts and welding units both account for only 0.4%. This data highlights that the most significant environmental impact in welding processes stems from consumables like welding wire and gas, indicating areas where sustainability efforts could be most effective.
The move comes as industries worldwide are under increasing pressure to align with stringent environmental regulations and carbon reduction targets.
You can access the full article at this link. 👇




Discussion